Electricity Unit Price in Pakistan November 2024
Electricity Unit Price in Pakistan have been a critical issue for many years. Whether it’s about running households, businesses, or industries, the cost of electricity significantly impacts everyone’s daily lives. Understanding how electricity prices are structured, what influences them, and what the current rates are in October 2024 can help people better manage their consumption and budgets. This guide will explain the electricity pricing system in Pakistan, the key factors behind the prices, government policies, and how these prices affect the general public.
Introduction to Electricity Pricing in Pakistan
Electricity Unit Price in Pakistan are determined by multiple factors, including the cost of fuel, government policies, and the efficiency of electricity generation and distribution. The electricity supply in Pakistan is handled primarily by state-owned companies like WAPDA (Water and Power Development Authority) and K-Electric in Karachi. These companies are responsible for generating, transmitting, and distributing electricity across the country.
As of October 2024, Pakistan continues to face challenges in meeting the electricity demand due to its dependency on imported fuel, aging infrastructure, and fluctuating international fuel prices. Understanding the current electricity rates and what causes them to rise or fall is essential for both consumers and businesses.
Electricity Unit Price for Various Distribution Companies in Pakistan (2024)
| Distribution Company | Number of Units | Per Unit Rate (PKR) | Additional Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Tariff | 1-100 | 39 | Applicable across most regions |
| 101-200 | 41 | Slight increase for higher consumption | |
| 201-300 | 42 | Mid-level consumption rates | |
| 301-400 | 43 | Standard tariff for mid-to-high usage | |
| 401-500 | 43 | Consistent rate for this bracket | |
| 501-600 | 43 | High consumption households | |
| 601-700 | 44 | Minor increase for very high consumption | |
| Above 700 | 45 | Highest tier for extensive use | |
| Peak Hours | Varies | Charges increase during peak hours |
FESCO (Faisalabad Electric Supply Company) Electricity Unit Price
| Number of Units | Electricity Per Unit Rate (PKR) |
|---|---|
| 1-100 | 22 |
| 101-200 | 27 |
| 201-300 | 30 |
| 301-400 | 33 |
| 401-500 | 35 |
| 501-600 | 36 |
| 601-700 | 37 |
| Greater than 700 | 42 |
GEPCO (Gujranwala Electric Power Company) Electricity Unit Price
| Number of Units | Electricity per Unit Price (PKR) |
|---|---|
| 1-100 | 22 |
| 101-200 | 32 |
| 201-300 | 37 |
| 301-400 | 43 |
| 401-500 | 47 |
| 501-600 | 49 |
| 601-700 | 52 |
| Greater than 700 | 65 |
HESCO (Hyderabad Electric Supply Company) Electricity Unit Price
| Number of Units | Electricity Per Unit Rate (PKR) |
|---|---|
| 1-100 | 41 |
| 101-300 | 58 |
| 301-1000 | 151 |
| Above 1000 | 188 |
IESCO (Islamabad Electric Supply Company) Electricity Unit Price
| Number of Units | Per Unit Price (PKR) |
|---|---|
| 1-100 | 16 |
| 101-200 | 22 |
| 201-300 | 27 |
| 301-400 | 32 |
| 401-500 | 35 |
| 501-600 | 36 |
| 601-700 | 37 |
| Greater than 700 | 42 |
LESCO (Lahore Electric Supply Company) Electricity Unit Price
| Number of Units | Electricity Per Unit Rate (PKR) |
|---|---|
| 1-100 | 10 |
| 101-200 | 13 |
| 201-300 | 24 |
| 301-400 | 27 |
| 401-500 | 37 |
| 501-600 | 38 |
| 601-700 | 41 |
| Greater than 700 | 42 |
MESCO (Multan Electric Power Company) Per Unit Price
| Number of Units | Electricity Per Unit Rate (PKR) |
|---|---|
| 1-100 | 4-7 |
| 101-200 | 10 |
| 201-300 | 12 |
| 301-700 | 19 |
| Greater than 700 | 22 |
SEPCO (Sukkur Electric Power Company) Per Unit Price
| Number of Units | Electricity Per Unit Rate (PKR) |
|---|---|
| 1-100 | 14.37 |
| 101-200 | 16.51 |
| 201-300 | 19.21 |
| 301-700 | 21.06 |
| Greater than 700 | 23.45 |
2. Breakdown of Electricity Tariffs
Electricity tariffs in Pakistan are categorized into different segments based on the type of consumer. Here’s how the electricity rates are structured for different user categories:
a. Domestic Consumers
Domestic users pay for electricity based on the number of units consumed. The pricing is progressive, meaning the more units consumed, the higher the rate per unit. Here’s a breakdown of the typical tariff for domestic consumers in October 2024:
- 1–100 units: PKR 12–14 per unit
- 101–300 units: PKR 16–18 per unit
- 301–500 units: PKR 22–24 per unit
- Above 500 units: PKR 28–30 per unit
Low-income households that consume less electricity are charged a lower rate, while higher consumption leads to higher costs.
b. Commercial and Industrial Consumers
Commercial and industrial electricity rates are usually higher than domestic tariffs due to the large-scale consumption involved:
- Commercial consumers: PKR 25–27 per unit
- Industrial consumers: PKR 20–22 per unit (depending on the type of industry)
The government provides certain subsidies to the industrial sector to encourage productivity and competitiveness in the global market.
3. Factors Affecting Electricity Prices
Several key factors influence electricity prices in Pakistan:
a. Fuel Costs
A significant portion of electricity in Pakistan is generated using thermal power plants that rely on imported fuel, including oil and gas. The fluctuations in international oil prices directly impact the cost of generating electricity.
b. Distribution Losses
Technical inefficiencies and power theft are major contributors to high electricity costs. Pakistan’s power distribution companies (DISCOs) face line losses that further burden the consumers.
c. Currency Exchange Rates
As Pakistan imports fuel for electricity generation, changes in the value of the Pakistani Rupee (PKR) against the US Dollar (USD) can cause fluctuations in electricity prices.
d. Government Taxes
The government levies various taxes, duties, and surcharges on electricity bills. These additional charges can significantly increase the total cost of electricity for consumers.
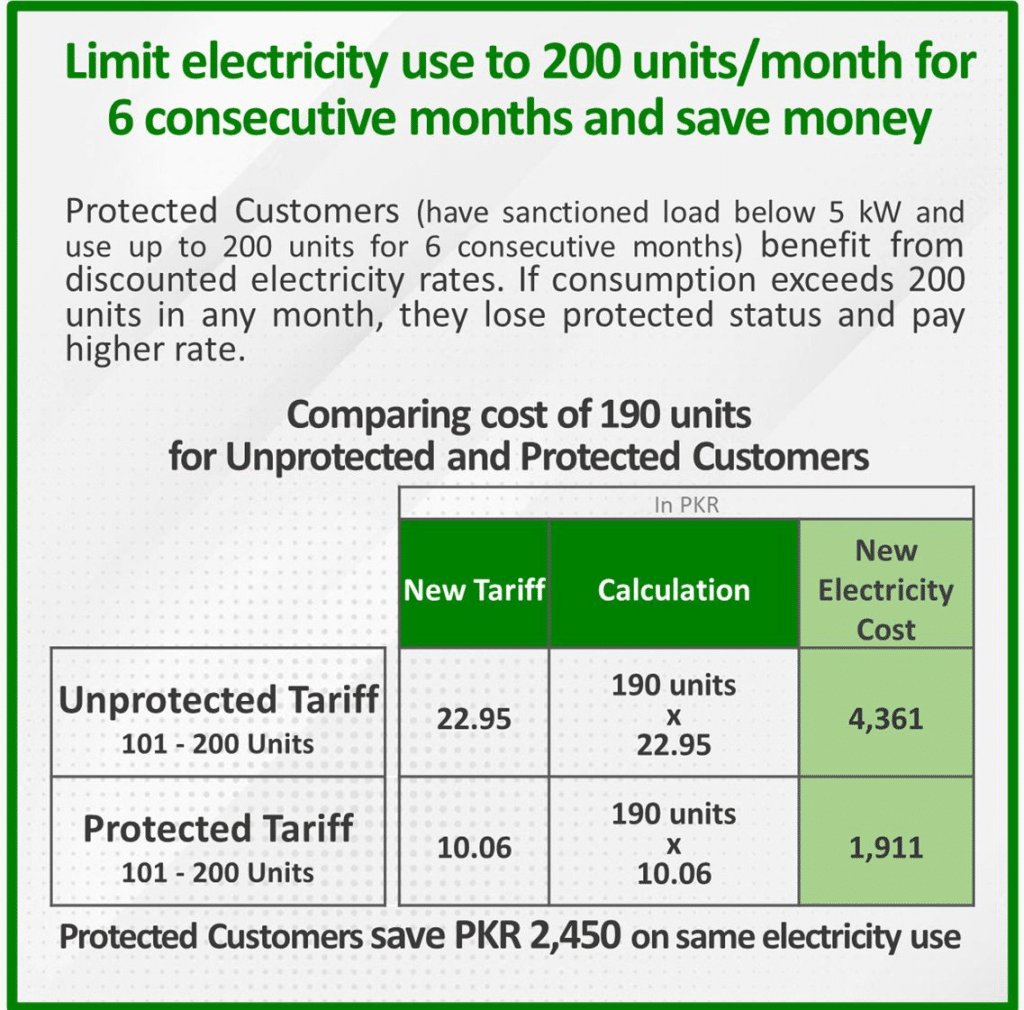
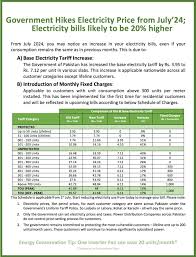
4. Government Policies and Subsidies
The government plays a crucial role in regulating electricity prices. Various subsidies are provided to protect low-income households from excessive charges. In October 2024, the government continues its efforts to balance the need for affordable electricity with the need for revenue generation to sustain the power sector.
Recent efforts include:
- Subsidized rates for users consuming below 300 units.
- Subsidies for the industrial sector to promote economic growth and maintain competitiveness.
The government is also working to reduce reliance on imported fuel by promoting renewable energy projects, which will eventually help stabilize electricity prices.
5. October 2024 Electricity Unit Prices in Major Cities
Electricity unit prices can vary from one region to another due to differences in distribution costs and regional infrastructure. Below are the estimated electricity prices for major cities in Pakistan as of October 2024:
Karachi (K-Electric)
- Domestic consumers: PKR 12–30 per unit (depending on consumption)
- Commercial consumers: PKR 25–27 per unit
- Industrial consumers: PKR 20–22 per unit
Lahore (LESCO)
- Domestic consumers: PKR 12–30 per unit
- Commercial consumers: PKR 25–27 per unit
- Industrial consumers: PKR 20–22 per unit
Islamabad (IESCO)
- Domestic consumers: PKR 12–30 per unit
- Commercial consumers: PKR 25–27 per unit
- Industrial consumers: PKR 20–22 per unit
6. Impact of International Fuel Prices
International fuel prices have always had a direct impact on Pakistan’s electricity prices, especially due to the country’s dependency on fossil fuels for power generation. The recent rise in global oil and gas prices has led to increased electricity unit costs in Pakistan.
In October 2024, the global fuel market remained volatile due to geopolitical tensions and the increasing demand for energy in the post-pandemic world. This uncertainty continues to affect electricity rates, with potential for further increases if fuel prices rise.
7. Role of Renewable Energy in Price Reduction
Renewable energy is becoming an increasingly important part of Pakistan’s energy mix. The government has set ambitious targets for increasing the share of solar, wind, and hydropower in the national grid. These renewable sources can provide cheaper and more sustainable electricity in the long term, reducing the country’s reliance on imported fuel.
In October 2024, several large-scale renewable energy projects are already underway, including:
- Solar farms in Sindh and Punjab.
- Wind power projects in the coastal areas of Pakistan.
These efforts are expected to bring down electricity costs over the next few years as renewable energy becomes a larger part of the grid.
8. Energy Crises and Load Shedding
Load shedding continues to be a challenge for Pakistan, particularly during the summer months when demand for electricity peaks. Shortages in fuel supply, aging infrastructure, and inefficient power plants contribute to these blackouts.
As of October 2024, major cities like Karachi, Lahore, and Islamabad still experience load shedding, although efforts are being made to reduce its impact.
9. Strategies to Save on Electricity Bills
To help mitigate the impact of rising electricity prices, consumers can adopt several strategies to reduce their energy consumption:
- Energy-efficient appliances: Using energy-saving LED bulbs, fans, and air conditioners can significantly reduce electricity usage.
- Time-of-use pricing: Some areas offer lower rates during off-peak hours, which can help save on bills.
- Solar energy systems: Installing solar panels can reduce dependence on the national grid and lower electricity costs over time.
10. The Future of Electricity Prices in Pakistan
The future of electricity prices in Pakistan depends on several factors, including the global fuel market, the success of renewable energy projects, and the government’s ability to reduce inefficiencies in the power sector. While prices are likely to remain high in the short term due to international market conditions, investments in renewables and grid improvements could help stabilize prices in the coming years.
11. Consumer Protection and Rights
Consumers in Pakistan have the right to fair and transparent billing practices. In October 2024, the government has implemented measures to ensure that consumers are not overcharged for electricity. These include:
- Regulation of meter readings to prevent inaccurate billing.
- Consumer courts for resolving disputes with electricity companies.
12. FAQs about Electricity Pricing
- What is the current electricity price in Pakistan (October 2024)?
- The price per unit ranges from PKR 12 to PKR 30 for domestic consumers, depending on consumption.
- Why is electricity so expensive in Pakistan?
- High fuel costs, distribution losses, and inefficiencies in the power sector contribute to the high cost of electricity.
- How can I reduce my electricity bill?
- You can save on your electricity bill by using energy-efficient appliances, reducing consumption during peak hours, and considering solar power systems.
- Is there any subsidy available for electricity consumers?
- Yes, the government provides subsidies for low-income households and the industrial sector.
- Will renewable energy reduce electricity prices in the future?
- Renewable energy projects are expected to lower electricity costs in the long term by reducing reliance on imported fuel.

